What is an ICC?
In the context of the POSH Act 2013 (The Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013), an ICC stands for Internal Complaints Committee. It is a mandatory body that every organization in India with 10 or more employees is required to constitute. The ICC is the primary mechanism within the workplace for addressing complaints of sexual harassment.
Breakdown of its Key aspects
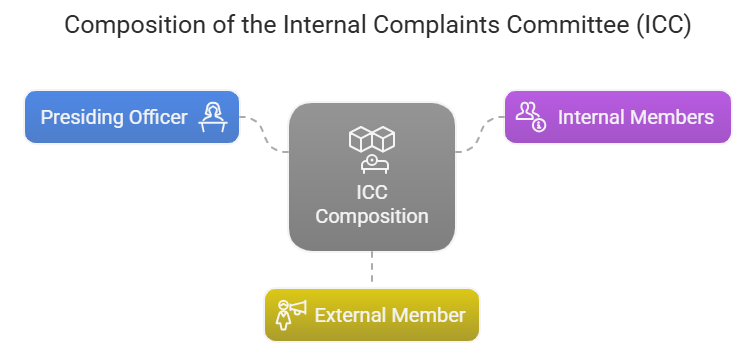
The POSH Act specifies the composition of the ICC, which should include:
- A Presiding Officer, who should be a woman employed at a senior level in the organization.
- two other members , employees of your organization who can be mature and unbiased to handle sexual harassment case also some have legal knowledge.
- At least one external member from amongst non-governmental organizations or associations committed to the cause of women or a person familiar with the issues relating to sexual harassment.
Why is it important and Mandatory?
The establishment of an Internal Complaints Committee (ICC) as mandated by the POSH Act 2013 is both important and mandatory for several critical reasons:
Why it is Important
- Establishes a Process for Resolution: The ICC offers a formal and internal platform for women employees to file complaints of sexual harassment and seek resolution within the workplace. Without it, they might lack a clear and accessible avenue for justice, potentially leading to underreporting and a continuation of harmful behaviour.
- Ensures Fair Inquiry: The ICC is tasked with conducting inquiries into complaints in a fair and timely manner, adhering to the principles of natural justice. This process aims to provide both the complainant and the respondent an opportunity to be heard and present their case.
- Promotes a Safe and Respectful Workplace: The presence of a functional ICC signals to all employees that the organization takes sexual harassment seriously and has a system in place to address it. This can contribute to a more secure, respectful, and productive work environment for everyone.
- Empowers Women Employees: Knowing that there is an internal body to address their grievances can empower women employees to speak out against harassment and feel more protected in their workplace.
- Contributes to Organizational Reputation: Organizations that comply with the POSH Act and have an effective ICC demonstrate a commitment to employee well-being and ethical practices, which can enhance their reputation and attract talent.
- Prevents Escalation and Legal Complications: Addressing complaints internally through the ICC can potentially prevent the escalation of issues to external legal forums, which can be more time-consuming, costly, and damaging to all parties involved.
- Facilitates Awareness and Prevention: The ICC is also often involved in promoting awareness about the POSH Act and conducting sensitization programs, contributing to a culture of prevention.
Why it is Mandatory?
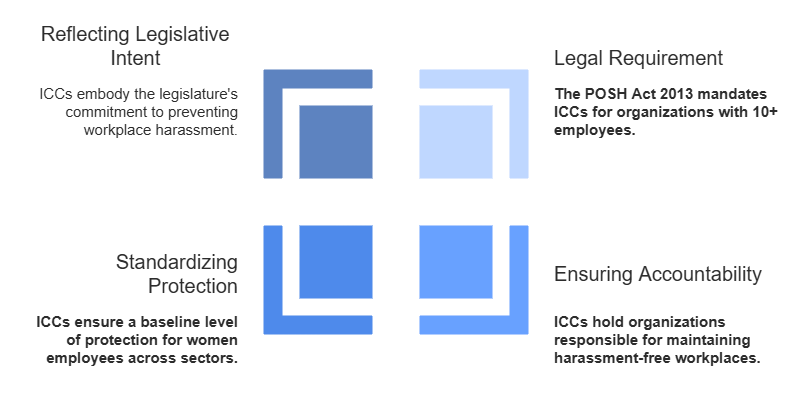
- Legal Requirement: The POSH Act 2013 explicitly mandates that any organization with 10 or more employees must constitute an ICC. This is a statutory obligation, and non-compliance can lead to penalties and legal repercussions for the employer.
- Ensuring Accountability: The mandatory nature of the ICC holds organizations accountable for creating and maintaining a workplace free from sexual harassment. It prevents employers from neglecting this critical aspect of employee safety and well-being.
- Standardizing Protection: Making the ICC mandatory ensures a baseline level of protection for women employees across different organizations and sectors in India. It aims to address the systemic issue of workplace sexual harassment.
- Reflecting Legislative Intent: The mandatory requirement reflects the legislature's strong intent to prevent and address sexual harassment at the workplace and to provide a clear framework for doing so.
In summary, the ICC is not just a recommended best practice but a legally mandated and crucial component for ensuring a safe, respectful, and equitable workplace for women employees in India. It provides a mechanism for redressal, promotes a culture of accountability, and aligns with the legislative intent to combat sexual harassment.
Why is it important and Mandatory?
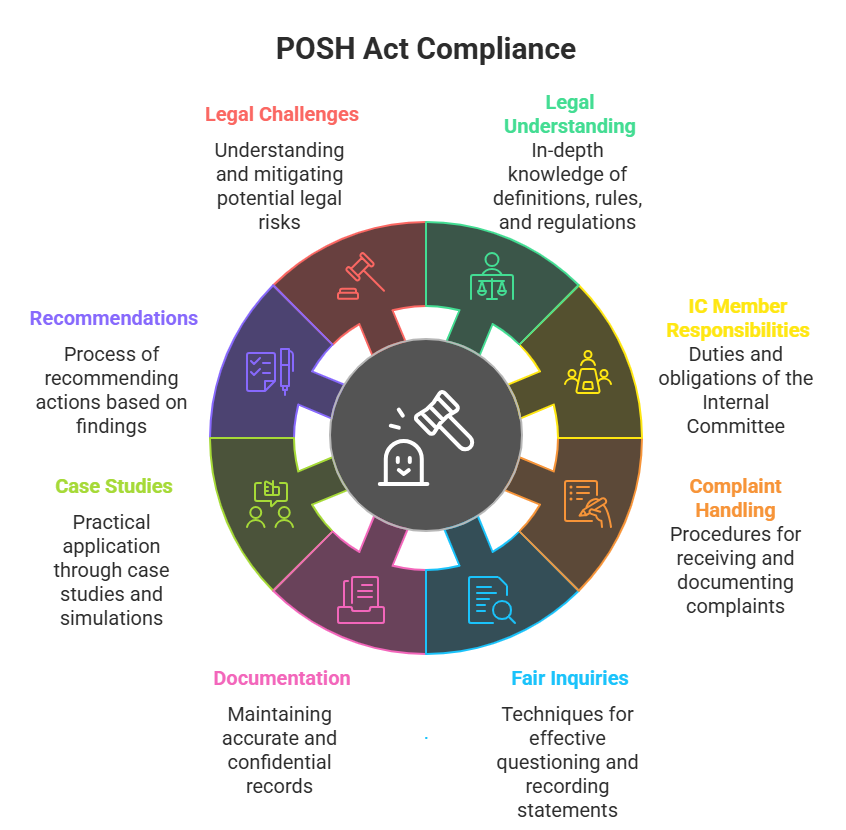
- In-depth Legal Understanding of the POSH Act
- Detailed analysis of definitions, rules, and regulations.
- Understanding employer obligations and liabilities.
- Recent amendments and case laws (if relevant).
- Role and Responsibilities of the IC Member
- Detailed breakdown of duties and obligations.
- Principles of natural justice and fair inquiry.
- Maintaining impartiality and objectivity.
- Ensuring confidentiality throughout the process.
- Procedures for Handling Complaints
- Step-by-step guidance on receiving and documenting complaints.
- Conducting preliminary assessments.
- Planning and executing inquiries.
- Gathering evidence and interviewing parties involved.
- Conducting Fair and Impartial Inquiries
- Techniques for effective questioning and recording statements.
- Dealing with sensitive information.
- Adhering to timelines and procedures.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping
- Importance of maintaining accurate and confidential records.
- Preparing inquiry reports and recommendations.
- Compliance with annual reporting requirements.
- Case Study Analysis and Simulations
- Practical application of the Act and procedures through case studies.
- Role-playing exercises to simulate inquiry proceedings.
- Recommendations and Conciliation
- Understanding the process of recommending actions based on inquiry findings.
- Exploring the possibility of conciliation (if applicable and agreed upon).
- Legal Aspects and Potential Challenges
- Understanding potential legal challenges and how to mitigate risks.
- Importance of adhering to the principles of natural justice.
For Senior Leadership and Management
- Building a Zero-Tolerance Culture
- Leadership's role in promoting a respectful workplace.
- Communicating the organization's commitment to POSH.
- Setting the tone from the top.
- Legal Obligations and Employer Liability
- Understanding the legal responsibilities of the organization and its leaders.
- Consequences of non-compliance.
- Risk mitigation strategies.
- Implementing and Monitoring POSH Policy
- Ensuring the policy is effectively implemented and communicated.
- Monitoring compliance and addressing any gaps.
- Supporting the functioning of the Internal Committee.
- Creating a Supportive Environment for Complainants
- Ensuring a safe and non-threatening environment for reporting.
- Providing necessary support and resources.
- Addressing Systemic Issues
- Identifying and addressing any underlying issues that may contribute to harassment.
- Promoting a culture of inclusivity and respect.